Glycine, an amino acid with the simplest chemical structure among all amino acids, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. While it is a non-essential amino acid, meaning the body can synthesize it on its own, glycine also offers a range of health benefits that have led to its incorporation into various applications. Here are the top five uses of glycine:
Neurotransmitter Regulation
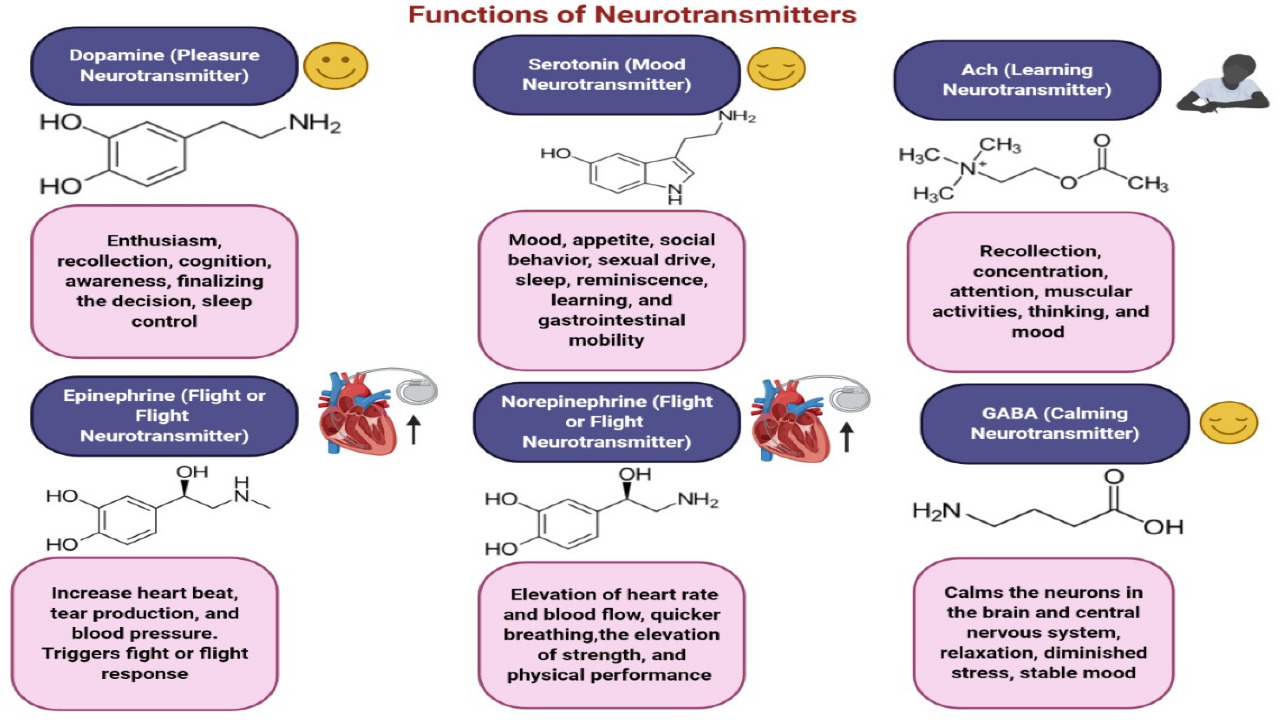
Glycine (glycin) serves as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It plays a vital role in balancing excitation and inhibition in the brain, contributing to overall cognitive function. Glycine receptors are involved in regulating motor function, pain perception, and sensory processing. Additionally, glycine has been studied for its potential in managing certain neurological disorders, including schizophrenia and epilepsy.
Sleep Improvement
Glycine has been recognized for its potential to enhance sleep quality. Studies have shown that glycine supplementation can improve subjective sleep quality, reduce sleep onset latency, and enhance daytime alertness. By acting on neurotransmitter receptors, glycine can have a calming effect, aiding in relaxation and contributing to better sleep patterns.
Collagen Production
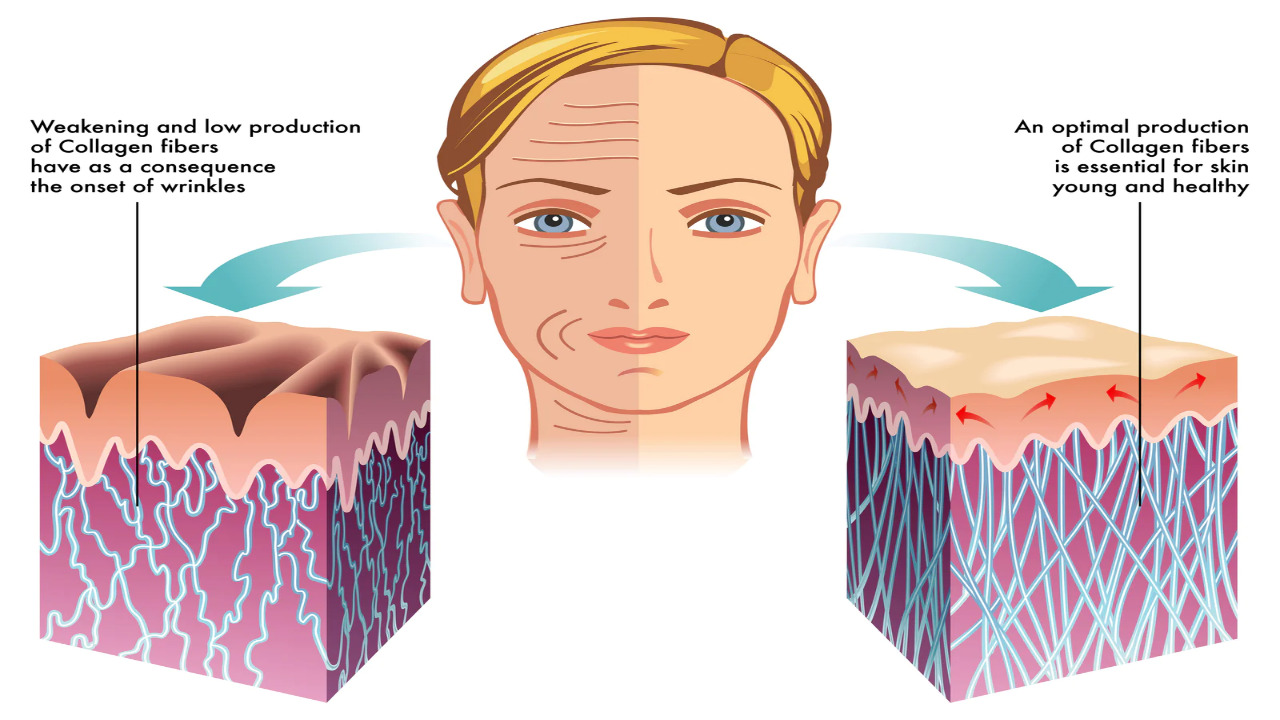
Glycine is a key component of collagen, a protein essential for maintaining the health and integrity of various tissues, including skin, bones, tendons, and cartilage. Collagen provides structural support and elasticity to these tissues, promoting healthy aging and wound healing. As a result, glycine supplementation or consumption through dietary sources can contribute to maintaining skin elasticity, joint health, and bone strength.
Sports Performance and Muscle Growth
Glycine plays a role in the synthesis of creatine, a compound that provides energy to muscles during short bursts of high-intensity exercise. Some research suggests that glycine supplementation may support muscle growth, exercise performance, and recovery by aiding in the synthesis of creatine. Moreover, glycine’s anti-inflammatory properties might assist in reducing exercise-induced inflammation and muscle soreness.
Gut Health
Glycine is involved in the synthesis of bile salts, which aid in digestion and the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins in the intestine. Additionally, glycine has been studied for its potential to support the integrity of the intestinal barrier and reduce inflammation in the gut. These properties make glycine relevant to gut health and may have implications for conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
It’s important to note that while glycine offers various potential benefits, individual responses can vary. As with any supplement or dietary modification, consulting a healthcare professional before adding glycine to your regimen is advisable, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
In conclusion, glycine is an amino acid with a diverse range of applications, contributing to neurological health, sleep quality, collagen production, sports performance, muscle growth, and gut health. Its multifaceted role in various physiological processes makes it a valuable component for overall well-being. As scientific research continues to unfold, we can expect further insights into the intricate ways in which glycine impacts human health and potential new uses for this amino acid in medical and therapeutic contexts.

